Connectors
Apple Computer designed the FireWire computer to digital device connection. These
connectors have also appeared on the backs of some HDTV compatible sets.
In December 2002, a new standard specification called high-definition multimedia
interface (HDMI) was submitted. It is a user friendly jack that is smaller than a
DVI and carries multi-channel audio along with the video. These should be common
on HDTV sets by 2004 and we may see the end of DVI connectors on new HDTV displays
(www.soundandvision.com).
In addition to video jacks, there are speaker jacks to learn about.
Understanding the terminology and becoming familiar with what's on the market allows
intelligent decisions to be made. Making the right connection is essential in configuring
a new system.
If there's a question, try looking at the specifications listed for an item of interest.

Left to right photos show connectors for DVI, s-Video, RF, composite, and two forms
of component for HDTV (YPbPr or RGB) (photos from www.optomatv.com).
Problems with flat screens
Plasma displays can be big and heavy in addition to being hot. Plasma phosphors
use a lot of power because they are inefficient in converting electrical energy
to light (www.emedialive.com).
LCDs have a problem producing true black, giving a dark gray instead. They also
show distinct pixelization and have a narrower viewing angle than plasma
(www.soundandvisionmag.com).
LCoS is much more expensive than current competitive formats.
DLP technology in the single-chip sets often get a "rainbow"
effect. This can be corrected by using faster color wheels (Sound
and Vision magazine).
|
Resolution
The NTSC standard for scan lines is 525 but conventional displays only show 480
lines. Advertised resolution often refers to the horizontal direction that, when
displayed or printed, is composed of dots. In addition, these values are for
grayscale and are much less if color resolution is referenced.
Resolution lines are supposed to be measured across the largest circle that will
fit into the area being measured. Resolution expressed in pixels is the measurement
of the whole height or width of the screen. There are fewer vertical lines than
the number of scan lines (members.aol.com/ajaynejr).
The original image is at top left. Top right is a video representation. The bottom
left image shows how poorer horizontal resolution would look while the bottom right
shows poorer vertical resolution (graphic from members.aol.com/ajayne).

Allan W. Jayne states, "The rule of 80 lines of resolution for every
megahertz of bandwidth (for NTSC) is measured from the carrier frequency to
one side only, i.e. the larger sideband when dealing with modulated signals."
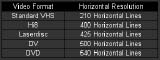
Resolutions vary for different types of video formats (www.divx.com).
|
|
Digital Light Processing (DLP) is a fixed-pixel technology developed by
Texas Instruments that uses a digital micromirror devices (DMDs) (Sound and
Vision magazine, diagram by Dimitry Schidlovsky).
See the light with TI micromirrors
|
|
|
Texas Instruments has developed a technology called digital light processing
(DLP) which uses their digital micromirror devices (DMDs) in video displays.
The DLP is used for projection televisions in addition to flat television
displays.
According to www.dlp.com, a DLP is described as a chip containing tiny mirrors
that are less than one-fifth the size of a human hair. The DLP is made of a
rectangular shaped array of up to 1.3 million hinge-mounted DMDs. Each
micromirror acts as the equivalent of one pixel.
Micromirrors are turned toward or away from a light source. When the
mirrors are moving, it's like turning a light switch on or off. The chip is coordinated
with a graphic or digital video signal to project a grayscale image. The gray
intensity is determined by how many times the light hits
the mirror in a specified timeframe. The more light, the lighter the gray color will
appear after the white light is reflected.
The resulting white light is passed
through a color wheel to produce over 16.7 million colors when using a 1-DMD chip.
The chip has a 16:9 aspect ratio.
|
Another chip used for cinema production quality is a 3-DMD chip. One DMD is used
for each red, green, or blue, respectively, to create more than 35 trillion colors.
"...an array of up to 1.3 million hinge-mounted DMDs."
|
A big advantage that DLP has in a flat video display is that it does not suffer
from "burn in" that has plagued computer monitors with images left on
for a period of time.
This year, TI's Digital Light Processing received an Emmy award for "Outstanding
Achievement In Engineering Development." The inventor of the DMD and TI employee,
Larry Hornbeck, Ph.D., also received an Emmy.

Texas Instruments's DMD (Digital micromirror
device) tilts toward or away from light to create grayscale images (www.dlp.com).
|
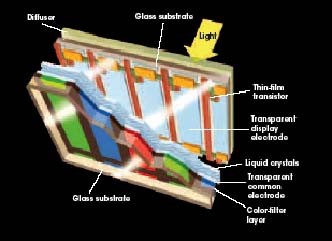
Liquid-Crystal Displays (LCD) have evolved from use in calculators and
watches to larger applications, such as video displays (Sound and Vision
magazine, diagram by Mark Schrieder).
LCD fixed-pixel display
Liquid-crystal displays (LCD) have been around for a while in watches, calculators,
and cell phones. Some video displays also use this liquid-crystal technology.
There is no light emitted by an LCD. Fluorescent light behind the liquid-crystal
display shines through the pixels to form an image (www.emedialive.com).
Sound and Vision magazine describes the way liquid-crystal displays work as,
"A matrix of thin-film transistors (TFTs) supplies voltage to liquid
crystal-filled cells sandwiched between two sheets of glass."
Three dots (red, green, and blue) make up one pixel that is hit with an electronic
charge that un-twists the crystals to allow a certain amount of light through
(www.soundandvisionmag.com).
These displays continue to be popular, even with all the competition in flat-panel displays.
|

